
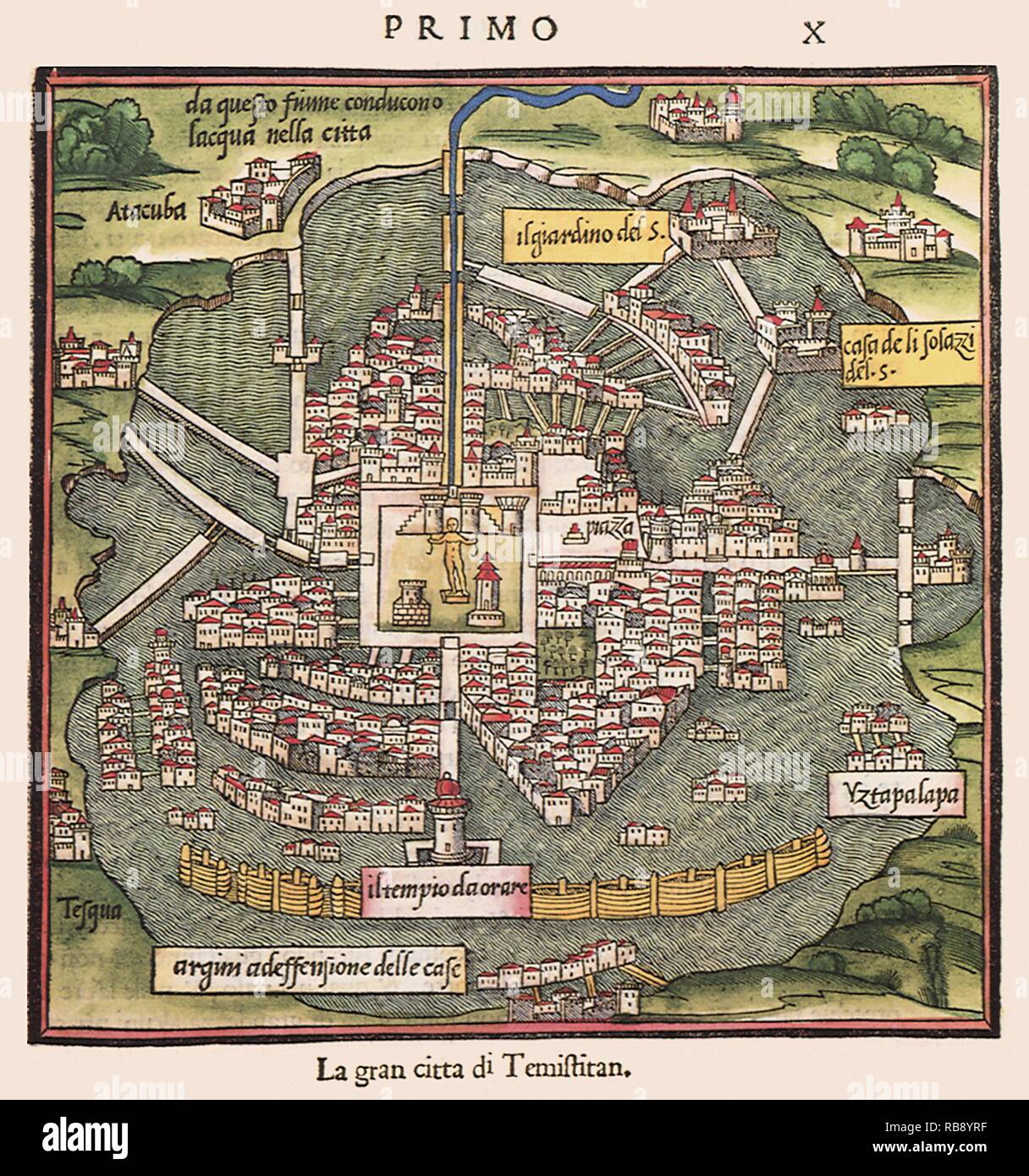
Barges collected garbage along the canals and took it outside of the city and private homes and public spaces both had latrines. Tenochtitlan's sanitation infrastructure was superior to that of many modern cities. Waterways were left between each of the Chinampas that served as a comprehensive canal system (similar to that of Venice) in which canoes carried people, food, and other items to almost every part of the expanding city. Chinampas (seen in the Agriculture topic) were built on the lake further and further from the main island, a gradual terraforming project that greatly increased the area of the city. Engineers built two aqueducts, each over four meters long, to carry fresh water into the city from nearby springs. Three earthwork causeways connected the island to the mainland and facilitated the constant movement of goods, tribute, and people to and from the capital.

The city's interior had both impressive architectural works, especially the sixty meter Templo Mayor, and centers of culture and scientific learning like Moctezuma's zoo and gardens. Perhaps inspired by the long-abandoned nearby ruins of Teotihuacan, the Aztecs built their city on a rectangular grid that expanded outwards from the temple complex in the center. Tenochtitlan, founded on a swampy island in Lake Texcoco around 1325, rivaled the greatest capitals of contemporary Europe and Asia in size, population, and beauty and, within two centuries of its founding, had become the administrative and religious center of a powerful expansionist empire.įrom an engineering point of view, the city was a marvel, especially considering the inherent challenges of building on a lake without abundant freshwater or agricultural land.

The Aztecs, in one of the most spectacular applications of science and technology in the pre-modern world, transformed a brackish lake into a metropolis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
